Table of contents
- Introduction
- Introduction
- Chapter 1
- Section 1: Exploring eXtreme Programming
- Section 2: Philosophy of XP
- Related subjects
- References
Delving into Extreme Programming: An In-depth Review of 'Extreme Programming Explained' (2nd Edition)
The content here is under the Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license
Join Our Community
Connect with developers, architects, and tech leads who share your passion for quality software development. Discuss TDD, architecture, software engineering, and more.
→ Join SlackTLDR
Extreme Programming (XP) is a software development methodology emphasizing response to change and technical excellence. It bridges the gap between SCRUM’s popular agile framework and technical practices. Kent Beck’s book explores XP’s values, principles, and practices, promoting collaboration, simplicity, feedback, courage, and respect. Chapters delve into diverse aspects like planning, testing, design, and scaling. XP’s roots in industrial engineering philosophies like Taylorism and the Toyota Production System highlight its evolution towards adaptable, value-driven software development. Emphasizing continuous improvement and human-centric approaches, XP challenges traditional notions of productivity and certification.
Introduction
Extreme programming (XP) (Beck & Andres, 2004) is a methodology focused on the technical and social aspects of software development. It focuses on two main pillars: response to change and technical excellence.
Technical excellence is the structure that allows teams to be agile. On the other hand, SCRUM is the methodology that got traction and is the most adopted by the industry as a means to “be agile”. Therefore, as already explored by Martin Fowler SCRUM has a place in the party, but is not the main course.
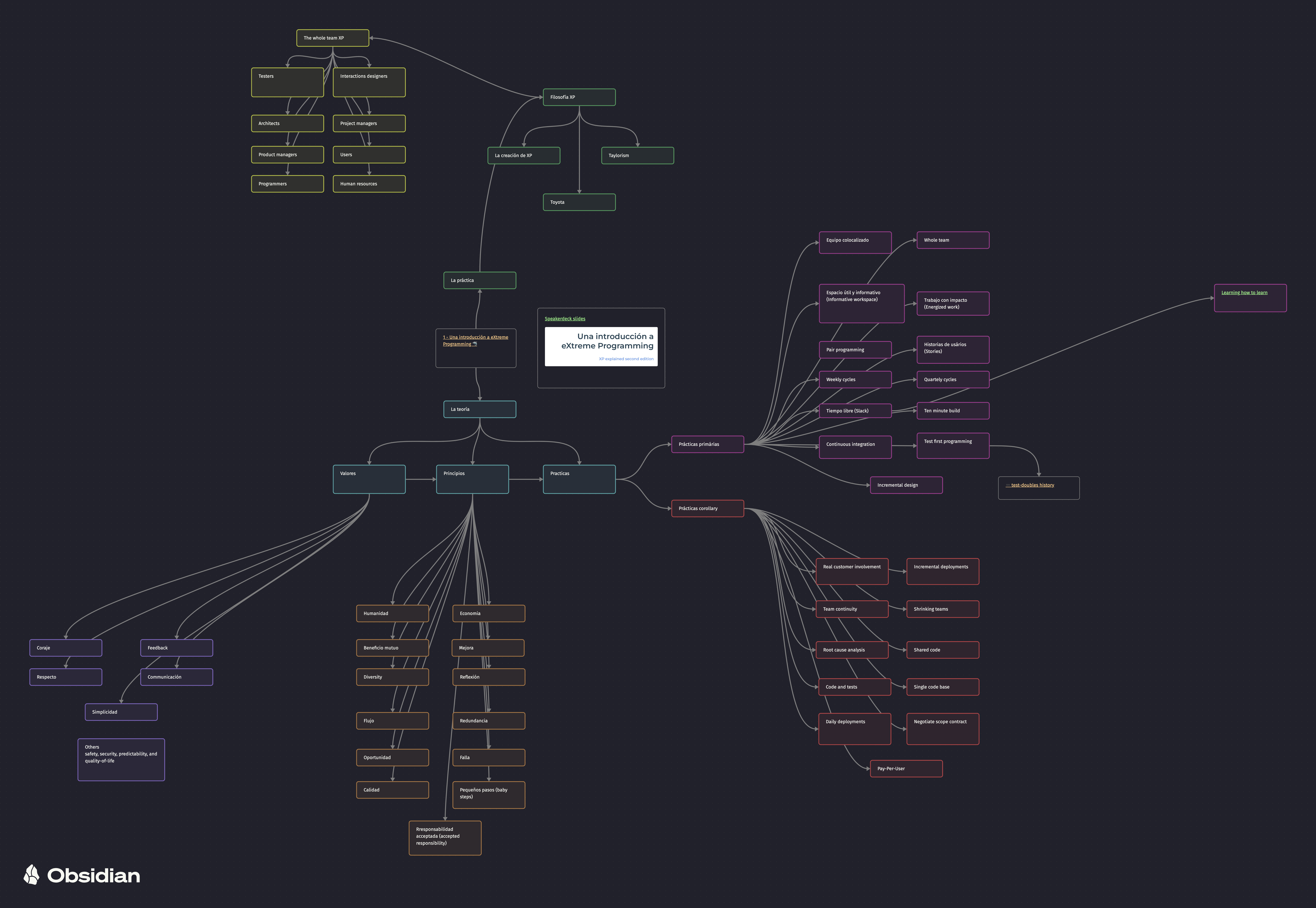
Kent Beck popularized different technical practices on writing XP and this post aims to go over the book and his contribution to the industry about software development. XP is the glue between the practices of SCRUM and the technical side, XP fills in the gaps that SCRUM left behind. Alongside this post, there is a mind map as well, that can be explored here, or through the embedded canvas that follows:
With that small introduction, let’s delve into the book’s content.
Chapter 1
The first chapter starts defining in a nutshell what eXtreme Programming is through values and practices, in the first section, this is what defined XP:
- A philosophy of software development
- A body of practices proven to improve software development
- Techniques to translate values into practice
- A community that shares many values and the same practices
Exploring eXtreme programming
Chapter 2
In this second edition, Kent Beck starts with an analogy of learning to drive and the change that occurs in software development. At first, it seems that there is no relationship between driving and coding until the moment comes and one realizes that both are related to adapting to change - Beck describes that as: Stay aware. Adapt. Change.
Customers are the ones that drive the system content - as the customer doesn’t know how to deal with software development she is the one in charge of pointing the right direction. As the dynamic improves and the team starts to work together and elaborate on their practices, each practice is an experiment to improve: effectiveness, communication, confidence, and productivity. Values are a key point to an extreme programming team.
Practices are clear. Everyone knows if I’ve attended the morning standup meetings. Whether I really value communication is fuzzy.
It is possible to relate the quote above with the daily stand-up meeting that any scrum team does, therefore, the argument of values is the one that sticks. The values are what we do and the values are what are what we do without prescription.
VALUES -------|------------|-------- PRACTICES
| |
| PRINCIPLES |
Bridging the gap between values and practices are principles.
Chapter 3
Practices are the things you do day-to-day, specifying practices is useful because they are clear and objective. Even with the best practices in place, it does not mean that one can be the best one in class, practices alone lack a key part in the process. Kent makes this analogy with a gardener.
The values are the glue that one can develop between the practice and the objective of becoming a professional. Values are the large-scale criteria we use to judge what we see, think and do. In other words, reading XP won’t make anyone a better programmer.
Chapter 4
This chapter is all about the values that an XP team embraces, let’s go over the key areas that Kent shared along with some personal notes on the matter:
-
Communication is what matters the most for a software development team.
- Communication is important for creating common sense and effective cooperation.
-
Simplicity is hard work. This is not to think simple, rather, it is focused on eliminating wasted complexity.
- Simplicity is dependent on the context.
- This value becomes even clearer in the practice of Test Driven Development which deescalate the complexity one might start to implement software.
- Improving communication helps achieve simplicity.
- Simplicity also comes from experience as the career progresses experienced developers tend to find simpler solutions over complicated ones.
-
Feedback is eminent in an environment that changes.
- We might not know how to do it right.
- What is right for today might be wrong for tomorrow.
- Being satisfied with improvement rather than expecting perfection.
- XP teams generate as much feedback as quickly as possible - watch out for too much feedback.
-
Courage is effective action in the face of fear, courage can manifest itself sometimes with action and sometimes with patience
- The courage to speak truths, please and unpleasant, fosters communication and trust.
-
Respect is the act of caring about others.
- Software development has an equal value as a human being.
- The contribution of each person on the team needs to be respected.
Chapter 5
Humanity
This section is as fundamental as the other parts of the book, however, humanity, might tend to click later on for professionals applying XP. Early in the book, this practice demonstrates that XP requires a bit of experience to grasp it fully. Thinking and caring about humanity tend to develop late in the career path.
- Software development doesn’t meet human needs
- What do people need to be a good developer?
- Basic safety and freedom
- Accomplishment
- Belonging
- Growth
- The ability to understand and be understood
In conclusion, Kent Beck in the book states that XP meets business and personal needs.
Economics
- Make sure what you are doing, meets business goals and serves business goals.
- Software development is more valuable when it earns more money sooner and spends money later.
- do not invest in speculative flexibility.
Mutual benefits
- Extensive documentation violates mutual benefits
- XP uses the following to give mutual benefits:
- Automated tests help to design and implement better today.
- Carefully refactor.
- Choose names that are coherent and explicitly sets of metaphors.
- Resolve more problems that create new ones.
Self-similarity
- When nature finds a shape that works, she uses it everywhere she can. The same applies to software development.
- Just copying one thing to another context doesn’t mean it will work.
- Having the system-level tests before you begin implementation simplifies design, reduces stress, and improves feedback.
- For a long time in the industry, this is still the biggest challenge that I have encountered. Teams do not care about the system-level tests and rely on manual checks to test functionalities.
Improvement
- There is no perfect process.
- Don’t wait for perfection to begin. Put improvement to work by not waiting for perfection.
- Start the activity right away and refine the results over time.
Diversity
- A team where everyone is alike is not effective.
- Programmers should work together and value each other opinion.
- Brings new perspectives, and a variety of skills are needed to think about a problem and a solution.
Reflection
- Good teams take a step back to think about how they are working and why they are working.
- Feelings tempered by the intellect are a source of insight.
- Learning is action reflected.
Flow
- XP practices are biased towards a continuous flow of activities.
- Teams have suffered from big bang integration - everything at once instead of a continuous flow of delivery.
- Resolve the problems that disrupt the flow.
Opportunity
- Problems are learning opportunities.
Redundancy
- Defects corrode trust, you cannot solve the defect problem with a single practice.
- Having a testing phase after development should be redundant.
Failure
- Fail and learn.
- Failure is not a waste. Fail instead of talk.
Quality
- Sacrificing quality is not effective as a means of control. Projects don’t go faster by accepting lower quality.
- Time and cost are most often fixed. XP chooses scope as the primary means of planning. The scope is never known precisely.
- Do the job the best way you can.
Baby steps
- Are expressed in practices like test-first-programming and continuous integration.
Accepted responsibility
- Responsibility cannot be assigned only accepted.
- The person responsible for the story is responsible for the design, implementation and testing of the story.
Chapter 6
The goal for practices in the XP is to make progress towards an ideal state of effective development. The primary practices are useful independent of what else you are doing.
The corollary practices are likely to be difficult without first mastering the primary practices.
Chapter 7
Two kinds of approaches but they might vary based on the context:
- People that need planning because they don’t know what needs to be done
- People who need quality-related practices because they are creating too many defects
Sit Together
- develop in a space big enough for the whole team.
- the team was spending time in a cold and drafty room but they were successful.
- the problem is always a people problem.
- sit together to communicate with all our senses together.
- sit together even if it means traveling.
Whole team
- we belong.
- we support each other’s work, growth and learning.
- add and remove people from the team on demand
- 150 people more and it is not possible to recognize people to build trust and trust is needed for collaboration
Informative workspace
Make your workspace about your work. An interested observer should be able to walk into the team space and get a general idea of how the project is going in fifteen seconds.
- informative charts
- private and public space to work is needed.
Energized work
- Software development is about insights and insights come to the rested mind.
- do not overwork, keep track of when one might not be as productive as it can and stop for the day.
Pair programming
- Two people sitting at one machine.
- Clarify ideas.
- Take initiative if the partner is stuck.
- Hold each one accountable for the practices in the team.
- Rotate frequently.
- Be aware of cultural differences, personal space means different things for different people.
- Hygiene and health are important.
- Emotions at work should be about work.
- If you are not comfortable pairing with someone in the team talk about it.
Other things related to pairing:
Stories
- Early estimation is a key difference between stories and other requirements.
- short names for stories
- This idea of stories was later credited by Jeff Patron and Peter Economy in the book “User Story Mapping: Discover the Whole Story, Build the Right Product” (Patton & Economy, 2014) and also by Rodríguez et al. (Rodríguez et al., 2019)
Weekly cycles
- Plan work a week at a time
- review progress
- discuss priorities and pick the most important ones for the business
- break stories down into tasks
- working on weekends is not sustainable.
Quarterly cycles
Focus on:
- Identify bottlenecks.
- Initiate repairs.
- Plan the theme for the quarter.
- Focus on the big picture.
Slack
- 80/20
- programmer chosen task
- geek week
Ten-Minute build
- Keep the build under ten minutes
- Automated views without requiring manual intervention
Continuous integration
- Integrate things in no more than a couple of hours.
- integrate work after a pair session
There is a section dedicated to this Continuous Delivery - Foundation, Configuration Management, Continuous Integration, Implementing a test strategy, build and deployment scripting, and the commit stage.
Test-First programming
- Start anything with a failing test.
Another thing related to the test first:
Incremental design
- invest in the design of the system every day.
- Bring improvements gradually and not everything upfront.
- XP teams are confident in their ability to adapt the design to future requirements.
Chapter 8
It is interesting how Beck starts chapter 8 by talking about getting started with XP practices, he follows the conversation by exploring the idea of change. Changing too fast can be risky, on the other hand, change is needed to accomplish results.
Looking at what you want to achieve might be a good way to start, as Becks says: Look at what you want to achieve. Then, start using one of the practices: “Automate the build”, or “Test first all day”. Another scenario that might help is to focus on the task at hand, for example, there is an integration that is coming up and I am feeling nervous regarding the code and design. Pair programming is the practice that addresses technical collaboration.
It is interesting how Beck’s chapter starts about changing and before jumping into the next section he elaborates on the difficulty of change. Anyway, change always starts at home.
“Dictating practices to a team destroys trust and creates resentment”.
“Software development is capable of much, much more than it is currently delivering”.
I do agree with the sentences that Beck shared regarding software development. What I am writing down now is more than twenty years later the release of XP explained and still, software development, is not showing all the value it has to offer.
Some of those values are also expressed in the lack of communication between parties as well as the popularity that SCRUM has that puts less effort into the values and principles presented by XP trying to give a more formal definition of work for software development teams.
Chapter 9
Be mindful of implementing the changes before doing the preliminary work to address the needs, otherwise, you will have a disaster on your hands.
Real customer involvement
- Customers should be part of the team.
- Proxy customer leads to a waste of time.
- Customers won’t trust us if they know how software development is.
- Waste time covering up.
Incremental deployment
Beck is explicit on big release upfront or D-Day as it is called in the book, his personal experience depicts a disaster in trying to migrate a legacy system of contracts to a new one, failing to reproduce the new behavior, leading to his loss of the bonus he would receive for that change.
The Big Bang release brings difficulties to people and gets them too nervous trying to achieve everything that is needed for D-Day. If on D-Day everything works fine the problem is with the people, they will be too exhausted to be productive again.
Team continuity
K eep people that are doing great together, do not avoid the human aspect of it, but it does not mean static teams. Developers working on an XP team can join and leave a team and get productive after a month.
Shrinking Teams
Too many people on a team brings also challenges, too few members in different teams call for merging them.
Root-Cause Analysis
“Every time a defect is found after development, eliminate the defect and its cause.”
- Write an automated system-level test that reproduces the defect.
- Write a unit test with the smallest possible scope that also reproduces the defect.
- Fix the system, so the unit test works. Repeat till it works.
- Once the defect is fixed, figure out why the defect was created.
For the last one ask the five whys(This is inspired by Taiichi Ohno on the five whys).
This will lead to potentially the people’s problems lying around as the root cause. Regression testing is an alternative to prevent the problem from occurring again.
Shared code
Anyone on the team can improve the code at any time. Until the team has developed a sense of collective responsibility, no one is responsible and quality will deteriorate. Pair programming helps teams to demonstrate their commitment to quality. In that sense, Continuous Integration is also an important part of collective ownership.
Code and tests
Only the source code and the tests are permanent artifacts. Customers pay for what the system does today and what it will do tomorrow. The better the team is with incremental design the fewer design decisions it has to make up front.
Single code base
You can develop in a branch but never let it live longer than a few hours. There are some valid reasons to have different versions of the same code base (like other branches), therefore, it can lead to the overhead of having to apply a fix from a branch into another branch and retrofit the work already done.
Instead of creating many versions of the code base, fix first the underlying design problem.
Daily deployment
Everything that is on the programmer’s desk and what is in production is a risk. Deploy every night. There are some barriers to deploying frequently, some of them are technical and others are social, for example, the deployment process is so stressful that no one wants to deploy.
Chapter 10
eXtreme Programming is not about programming. It is about building software. The chapter goes over a feel of roles on the team, for example, testers, designers, architects, project managers, product managers, executives, technical writers, users, programmers and human resources. The collaboration needed in XP screams at us.
- Testers amplify communication in extreme scenarios beyond the happy path
- Designers clarify and write stories
- Architects look for refactoring, system-level tests and implement stories
- Project managers facilitate communication
- Product managers encourage communication between customers and programmers

- Executives support the team and encourage the team
- Technical writer’s early feedback and value for users
- Users write stories and make domain decisions
- Programmers estimate tasks, break stories into tasks, write tests, write code, automate, and improve design system
- Human resources emphasize teamwork and social skills

Chapter 11
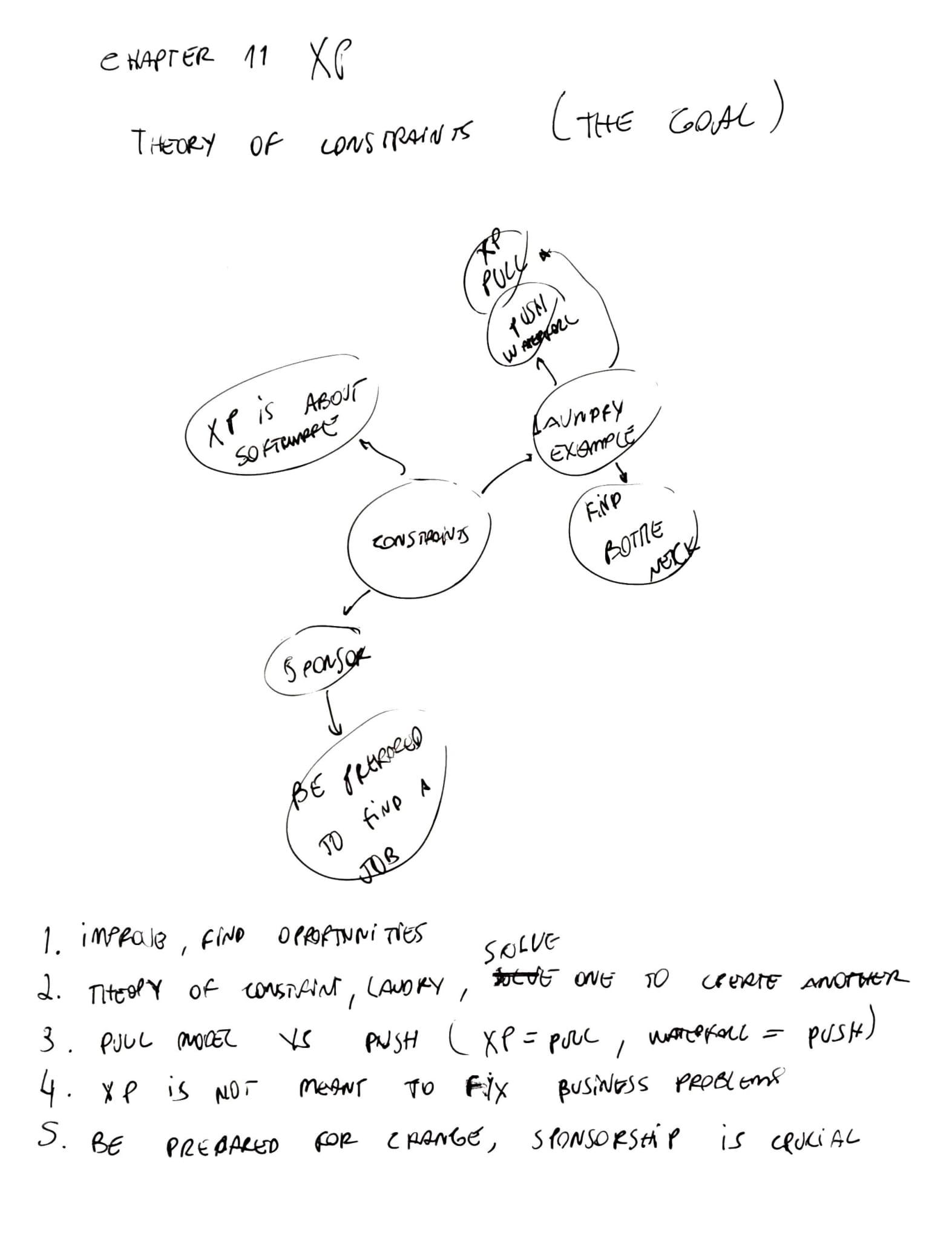
- Improve, find opportunities
- Theory of constraints, solve one to create another
- pull model versus push model - XP pulls and waterfall push
- XP is not meant to fix business problems
- Be prepared for change
- Sponsorship is crucial
Chapter 12
- Planning makes goals and directions explicit.
- In XP planning is like going to buy groceries.
- the prices are the estimates
- the budget the time available
- Planning decides what to do next
- estimates and costs are uncertain
- Planning is a daily activity and quarterly activity
- Plans are not predictions of the future
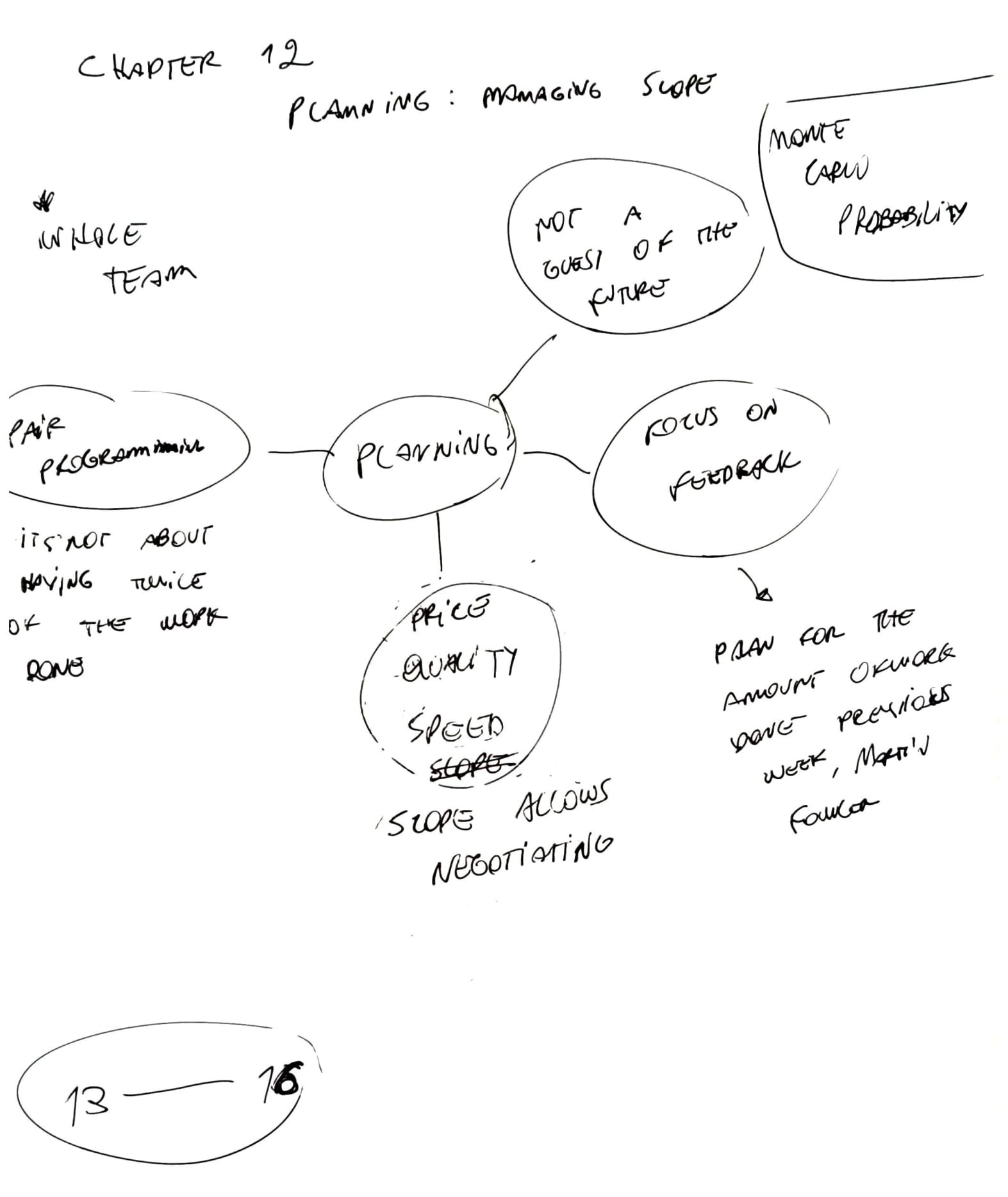
Manage the project by three variables: speed, quality and price. Usually, speed and price are set outside of the project leaving only quality.
- Quality is the only variable that can be manipulated
- Lowering quality doesn’t eliminate work
- Satisfaction comes from quality work
The scope is left out of the model, bringing it in we will have:
- we can adapt
- we can negotiate
Everyone on the team needs to be heard the team only commits to needs.
- planning is something we do together
- it is an exercise of listening, speaking and aligning goals for a specific period
- some teams bring over the customer to the planning
- estimates improve over time, it is normal to start widely wrong and improve over time
- XP’s first edition had estimated in points but in the second edition it was shifted to hours making the communication as clear and explicit as possible
- be prepared to deal with situations in which real results don’t match estimates
- inaccurate estimates are a failure of information, not values and principles
There are some related materials with estimation and story points:
- Escape velocity, better metrics for agile teams - Review (Lead time, Delivery frequency, Cycle time, Cumulative Flow Diagram, Code quality, Team joy and Forecasting)
- Why Software Estimations Are Always Wrong
Chapter 13
A dilema in software development:
- test increases costs but leads to fewer defects
- defects increase costs
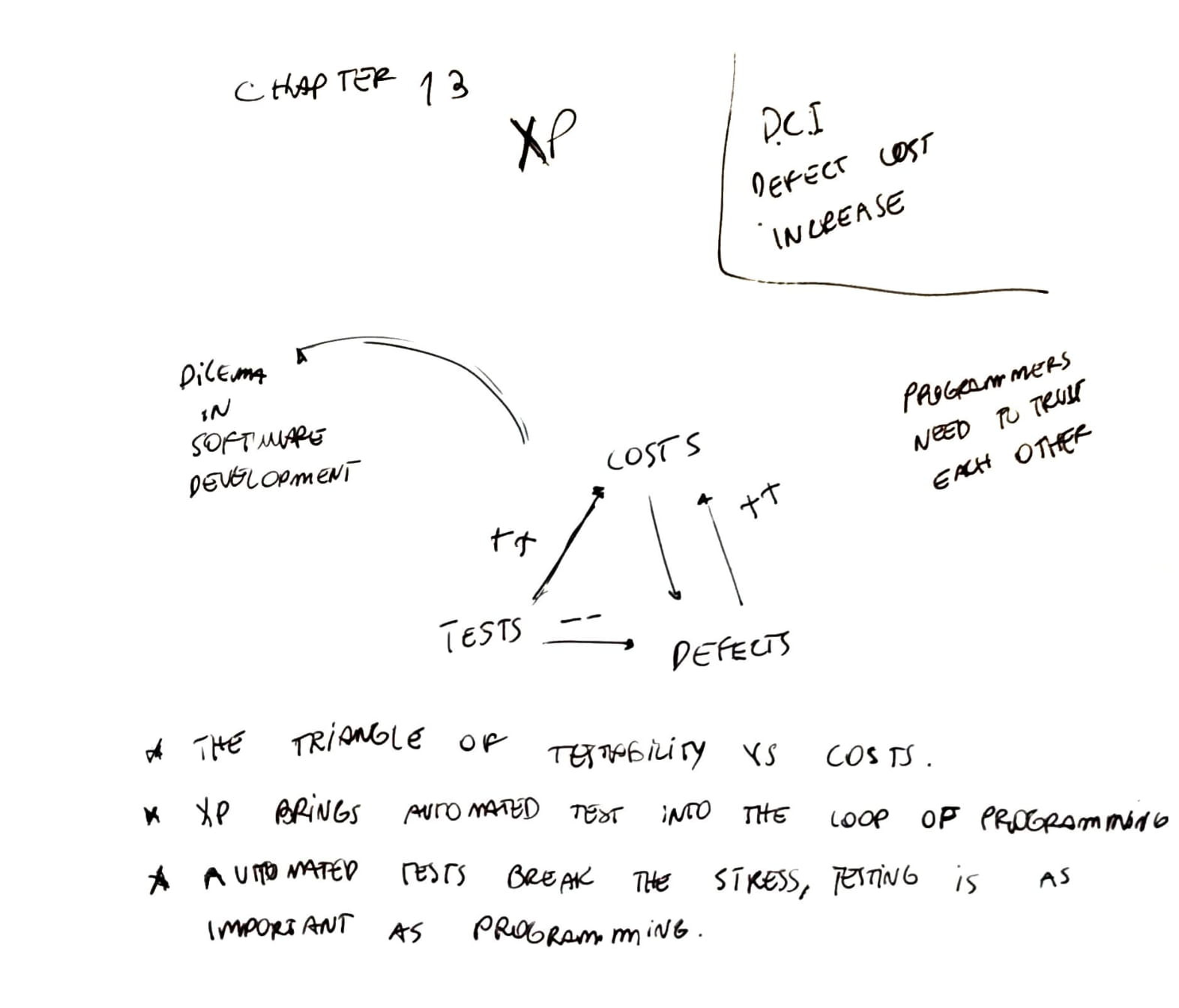
- extreme programming brings automated tests into the loop of programming
- automated tests break the stress
- testing is as important as programming
Chapter 14
Design as a tool for improvement leads to different approaches. In the world of software development, the cost of change is not set in stone. In the physical world, incremental change in the real world costs too much the steps in between add too little value.

Incremental design in software is valuable because often we are writing applications for the first time. Reversing a change when constructing a building is costly one day a change can cost $500 and the next day the same change can cost $10,000. In software reversing a day of work is trivial.
There is no option to not design because unconscious design will lead to failure. The most powerful design heuristic is to have “once and only once” a data or logic should exist only in one place. Quote extracted from the book around page 151 or so:
Most often, I didn’t improve the design because I was focused too narrowly on the problem of adding one more feature to the system. I didn’t try to balance the whole team’s productivity with today’s task. I didn’t think about how bad I felt jamming one more feature in where it didn’t belong. I didn’t think about how much motivation and satisfaction there is in doing a really good job.
For big systems that are legacy do not try to take everything at once, the key is to improve bit by bit. Part of the incremental design is to find a balance between delivering features and improving system design. In XP design decisions are deferred until they can be made in the light of experience. XP teams prefer simple solutions where possible.
Chapter 15
Often people relate to scaling as a human-only factor, in other words, scaling is adding more people. Therefore Kent argues other things to take into account while scaling:
- People
- Investiment
- size of the organization
- time
- problem complexity
- solution complexiy
- cnsequence of failure
Kent applies the “divide and conquer” to tackle the scalability issue:
- Check if a smaller team solves the issue
- if not, split the work among teams
Regarding investment, traditional accounting won’t work in software, it will create distortions. Find an ally in finance that can help you with that - Each company seems to account for software differently.

The challenge is to get everyone working together. XP is suited to close cooperation with specialists.
Problem complexity
Month after month the goal is to improve and become helpful in a way that the work done is much better than if it was done in a corner.
Solution complexity
- It is difficult to keep going when a team fixes an issue and creates three more.
- if you are fixing a defect in an area, clean up while you are there.
Consequence of failure
If we make mistakes, babies die. More than XP is needed in life-critical situations.

Chapter 16
Skipped - interview
Philosophy of XP
This section explores how other disciplines are connected to XP.
Chapter 17
Chrisley project case, project in trouble (also known as the XP story):
- it started with a phone call, someone was concerned about the payroll system performance - Kent Beck wrote a lecture on Smalltalk performance
- A project in trouble
- two months away from production
- listening to who was listening before answering
- people were tired

Three options were given to the project CIO:
- continue with the current project and never know when the software will be ready
- cancel the project
- start over from scratch with a smaller team
The last option was chosen.
Ron Jeffries was the first full-time XP coach
How will the project work:
- Three weeks iteration
- The customer has control over the priorities and which stories go first
- implement stories
- estimate stories
- figure how many fit
The project got delayed three months (April) and it was live for 3 years after Chrysler decided to decommission the project.
Chapter 18
Frederick Taylor industrial engineer. Taylorism assumptions.
- Things go according to a plan
- Micro optimizations lead to micro-optimization
- People are interchangeable and need to be told what to do

- Echoes of Taylorism can be heard in software development every time a person in authority changes an estimation from someone else.
- Taylorism also appears when someone creates a department of quality apart from development
Chapter 19
Toyota Production System (TPS) eliminates the rigid stratification found in the Taylorism factories.
Mary and Tom Poppendieck write extensively about the importance of product development part, like deliverying value through software.
- workers are accountable for the quality
- software development is full of waste of overproduction
Chapter 20
- Applying XP and seeing dramatic results takes a while more like years than weeks
- starting with XP is more like getting into a poll than adopting a child
- XP teams work differently and it can have negative social and political effects
- leading by example is powerful
- expecting others to do what you are not willing to try yourself is disrespectful
- learning is not a straight line
- Chose a coach: a good coach should encourage independence, not dependence

DO NOT USE XP if an organization’s values are: secrecy, isolation, complexity, timidity and disrespect.
Chapter 21
- There is no binary test for XP
- The goal is to successfully deliver projects and not the XP club pass
- Set expectations, saying you are “extreme” sets other’s people expectations of the way you work

- Without an authority holding the certification, it is just printing certificates and collecting money.
@KentBeck have you ever thought about a TDD certification?
— Marabesi 💻🚀 (@MatheusMarabesi) February 7, 2022
Chapter 22 and Chapter 23

Chapter 24

Chapter 25

Related subjects
- Behaviors To Avoid When Practicing Pair Programming
- Quantitative Survey on Extreme Programming Projects
- Pair Programming Illuminated
- Extreme Programming Installed
- Sustainable Software Development through Overlapping Pair Rotation - Last accessed Jun 20, 2023
- Una introducción a eXtreme Programming
- Extreme Hour
Social media
For further reference, the mindmap developed during the book reading was shared via social media:
this is a wip that I was building as we were reading xp 2ed in the @codurance book club, time to finish it up #craftatheart pic.twitter.com/o10R6uPG8o
— Marabesi 💻🚀 (@MatheusMarabesi) October 4, 2021
References
- Beck, K., & Andres, C. (2004). Extreme Programming Explained: Embrace Change (The XP Series). Addison-Wesley Professional.
- Patton, J., & Economy, P. (2014). User story mapping: discover the whole story, build the right product. " O’Reilly Media, Inc.".
Changelog
- Apr 16, 2024 - Added reference to under Related subjects and TLDR section