Graphql vs rest
The content here is under the Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license
Join Our Community
Connect with developers, architects, and tech leads who share your passion for quality software development. Discuss TDD, architecture, software engineering, and more.
→ Join SlackThis is a quick search done through Google Scholar using the keyword “REST versus Graphql”. The aim is to search for empirical data on the strengths and weaknesses of both approaches, as practitioners often argue that one is “better” than the other.
Introduction
Often, practitioners ignore that “best” might vary based on the context and level of knowledge of a given technology. This approach happens with the choice of using REST over GraphQL.
Approach to get information
- Search is set to use any time
- To sort by relevance and
- to be of any time
Top 5 papers in the result:
- REST vs GraphQL: A Controlled Experiment - https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.04761
- REST or GraphQL? A Performance Comparative Study - https://sci-hub.hkvisa.net/10.1145/3357141.3357149
- Additional material: https://speakerdeck.com/gustavopinto/rest-or-graphql-a-performance-comparative-study
- Experiences on Migrating RESTful Web Services to GraphQL - https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-91764-1_23
- Performance Analysis of GraphQL and RESTful in SIM LP2M of the Hasanuddin University - https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8878524
- Migrating to GraphQL: A Practical Assessment - https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8667986
Discussion
In this section, we will discuss the different features of each approach.
Data fetching
Data fetching is the most common theme when the subject is REST and GraphQL. Both offer different ways of consuming information. REST is based on the HTTP verbs to fetch data. Richardson’s Maturity Model explores the HTTP verbs more powerfully. The server is the one that offers different possibilities for fetching the data, such as filters and transformers. However, it is less common to see a RESTful API offering granularity over the data being returned. In other words, if the client doesn’t want the entire payload from a specific GET request, the server will return it anyway. This is the argument that gives GraphQL its foundation. GraphQL does offer granularity over the data being sent back from the server to the client. However, REST APIs can also implement this kind of behavior, but before GraphQL this was not common.
GraphQL, on the other hand, does not care about each different HTTP verb that the protocol offers. It uses only POST, and the GraphQL specification handles the different types of behaviors based on its language. To fetch data with GraphQL, queries are used. Those queries enable the client to specify what data it needs to retrieve, its properties, filtering, and transforming as well. GraphQL needs specific tooling to handle the complexity of dealing with its standard and language to communicate with clients and servers. The following are the most used ones:
- Apollo
-
Relay
- GraphQL playground explored how to use relay with code samples
Given that each type was created at different times, both are used today. However, GraphQL got its popularity with the appealing data structure that is sent from the server to the client as its main feature. Studies have shown that in a controlled experiment, GraphQL takes less time to implement in comparison with REST (Brito & Valente, 2020)
REST APIs, on the other hand, have also exploded in standardization. The OpenAPI, for instance, is the most used project with RESTful APIs. Examples of REST APIs:
Error handling
Handling errors in GraphQL is different from REST. In REST, errors are typically communicated through HTTP status codes, while GraphQL uses a standardized error response format that includes an array of error objects. This allows for more detailed error information to be returned to the client.
Tools to consume graphql
As with REST APIs, GraphQL can be consumed using different tools. The ecosystem created by GraphQL offers a variety of tools to consume and test GraphQL APIs. Let’s explore some of the tools used for working with GraphQL APIs out there that I have experienced. In this section, I will rate the tools from 1 to 5 based on my experience, considering factors like ease of use, features, and community support. 1 being the lowest grade and 5 being the highest.
Inmsonia
Insonia is a popular tool for APIs, including GraphQL. It provides a user-friendly interface for constructing and sending GraphQL queries and mutations, as well as viewing the responses. Insomnia supports features like environment variables, authentication, and response validation, making it a versatile choice for developers working with GraphQL APIs.
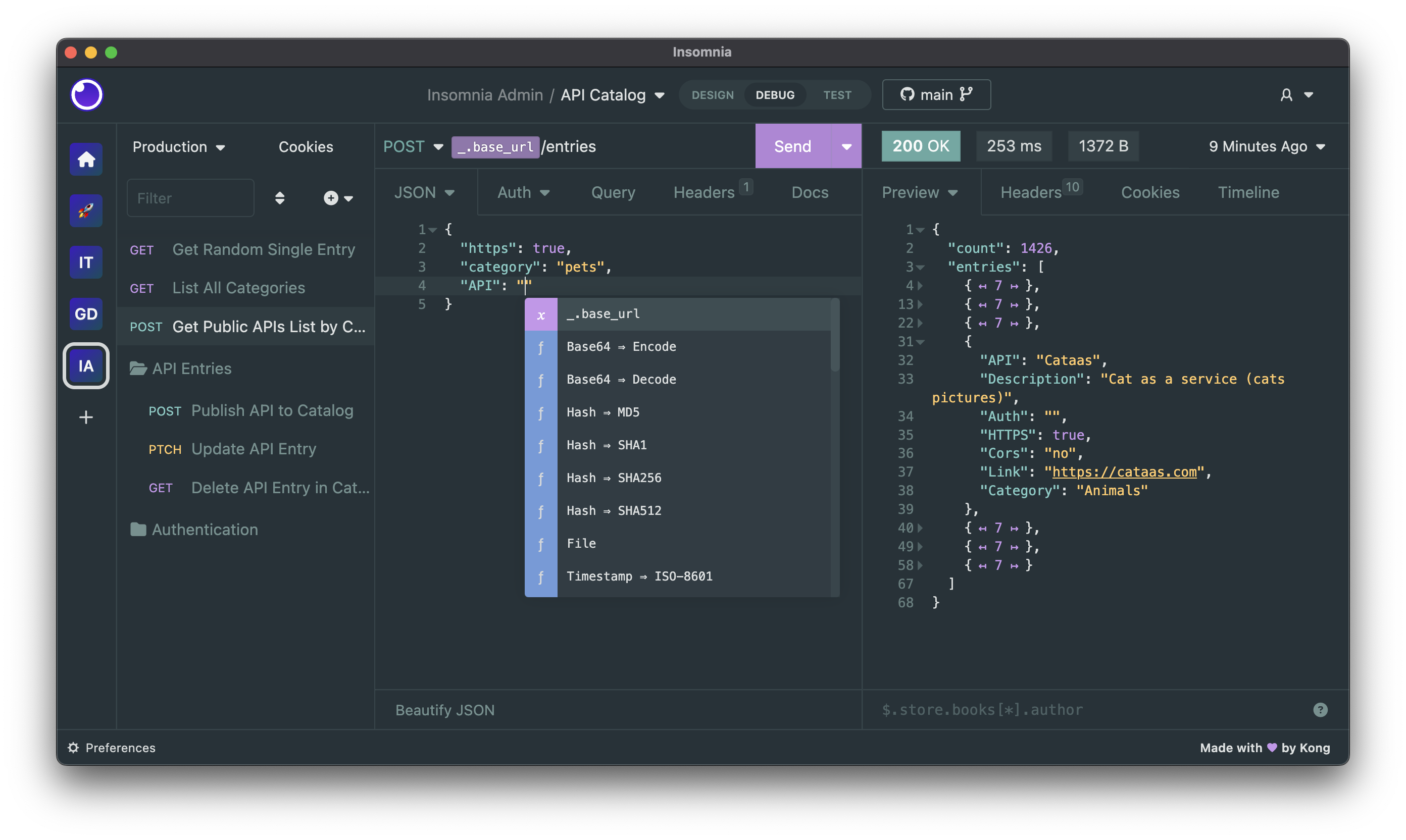
Insomnia also allows users to organize their requests into collections, making it easy to manage and share GraphQL queries and mutations. It supports GraphQL introspection, enabling users to explore the schema and available operations directly within the tool. Insomnia’s support for plugins and extensions further enhances its functionality, allowing developers to customize their GraphQL development experience.
| Factor | Rate |
|---|---|
| Ease of use | 5 |
| Features | 4 |
| Community support | - |
Postman
Postman is another widely used tool for API development and testing, including GraphQL. It offers a powerful interface for creating and managing GraphQL requests. Postman supports features like query variables, headers, and authentication for GraphQL APIs. It also provides a visual editor for constructing queries and mutations, making it easier to work with complex GraphQL schemas.
| Factor | Rate |
|---|---|
| Ease of use | 5 |
| Features | 4 |
| Community support | - |
Postman allows users to organize their GraphQL requests into collections, making it easy to manage and share queries and mutations. It also supports GraphQL introspection, enabling users to explore the schema and available operations directly within the tool.
intellij text HTTP
IntelliJ IDEA, a popular integrated development environment (IDE), includes built-in support for GraphQL. It provides features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and validation for GraphQL queries and schemas. IntelliJ also allows developers to execute GraphQL queries directly from the IDE, making it convenient for testing and debugging GraphQL APIs.
| Factor | Rate |
|---|---|
| Ease of use | 4 |
| Features | 2 |
| Community support | - |
Resources
Blogs that might complement content
- https://www.taniarascia.com/introduction-to-graphql
- https://escape.tech/blog/graphql-error-handling-a-security-pov
- Performance analysis of Web Services Comparison between RESTful & GraphQL web services - Bachelor Degree
- Exposing Rich Update Operations via REST APIs
- Testing
- https://miragejs.com/docs/advanced/graphql
Youtube videos/Talks
-
Comparing Native Java REST API Frameworks with Matt Raible
- This is a video that interests me since I gave a similar talk in the php ecosystem, comparing different frameworks when I was writing the Laravel book
- The video is not something related to graphql vs rest directly, but it talks about both of them and the support that each framework gives for each approach. I found it useful to see the comparison in the memory usage and startup time (even though it has nothing to do with the kind of api we are building it can make difference in the architecture)
- 15:09 - Introduction
- 18:51 - Why java
- 21:38 - Build REST API with java
- 26:00 - Get started with micronaut
- 30:48 - Get started with quarkus
- 34:13 - Get started with springboot
- 36:52 - Get started with Helidon
- 41:35 - What about GraphQL APIs
- 42:55 - Secure your API with OAuth 2.1
- 47:55 - What about testing
- 48:58 - Build with docker
- 52:21 - Go native with GraalVM - micronaut
- 52:46 - Go native with quarkus
- 53:02 - Go native with springboot
- 53:41 - Go native with Helidon
- 53:52 - Native startup time
- 56:56 - Native memory usage
- 58:31 - Demo time
- 01:14:55 - JHipster support
- 01:16:38 - Matt Raible thoughts
- 01:21:33 - Q&A
- This is the link for reference: Java REST API Showdown: Which is the Best Framework on the Market?
- Podcasts
References
- Brito, G., & Valente, M. T. (2020). REST vs GraphQL: A controlled experiment. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Software Architecture (ICSA), 81–91.